Read the history of the world in 3 minutes to help you gain knowledge!
For a long time, the Silk Road has been simply regarded as a trade channel connecting East and West. However, Peter Franco Pan, a professor at Oxford University, put forward a subversive view in his new book, The Silk Road: A Brand-new World History:
The importance of the Silk Road goes far beyond the trade channel. In fact, the Silk Road has shaped the past of mankind and will certainly affect the future of the world.
From four ancient civilizations, three religions and wars in human history to today’s the belt and road initiative, Franco Pan described the intricate relationship between the Silk Road and world civilization from ancient times to the present. The following excerpts from the Silk Road will give you three minutes to understand world history.
Silk Road and Four Ancient Civilizations
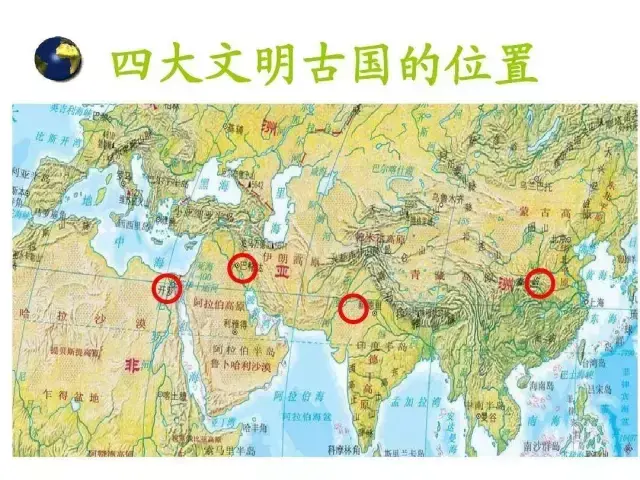
Ancient Babylon
Since the beginning of civilization, the Silk Road has been the cradle of empire. The Mesopotamian alluvial plain bred by the Tigris River and the Euphrates River provided soil for the emergence of human civilization, and it was here that the world’s earliest towns and cities were born. Almost 4000 years ago, King Hammurabi of Babylon promulgated the earliest written law in the world here.
Ancient Egypt
Ptolemy, the guard officer who accompanied Alexander the Great in his expedition, brought wealth from the Silk Road to Egypt and established a capital named Alexandria. According to a contemporary scholar, Alexandria has developed into the largest city in the world at that time, with a population of 300,000 in the 1st century BC.
Ancient India
Mohenjodaro, nearly 5,000 years ago on the Silk Road, is a miracle of the ancient world, with tens of thousands of urban population, criss-crossing streets and sophisticated sewage system, which cannot be compared with Europe thousands of years later. The Silk Road also linked India and Rome. A large number of coins found on the west coast of India can be traced back to the period of Augustus.
Ancient China
In the Han Dynasty, after many campaigns, China people drove the Xiongnu back to the grassland and seized the Hexi Corridor, which opened the door for a transcontinental communication channel-the "Silk Road" was born. The expansion of the territory aroused China people’s interest in the outside world, and the high-priced silk trade made China people get rich returns.
The Silk Road and Three Major Religions
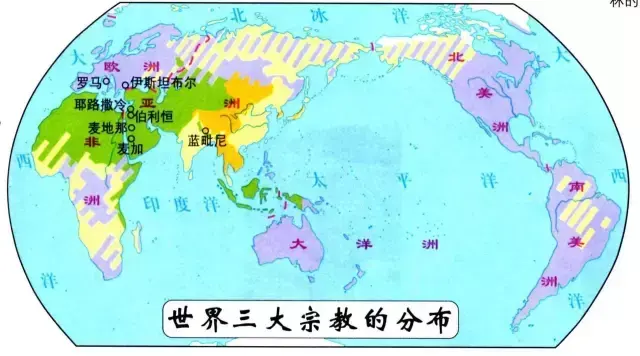
Buddhism
The scenery of cultural exchange on the Silk Road is amazing. In India, it was not until the worship of Apollo was established that the statue of Buddha began to appear: the statue seems to be based on the image of Apollo, which shows the deep influence of Greek culture. Before that, Buddhists were never willing to show their faces and make public, but now religious competition forces them to reform and innovate.
Christianity
Christianity spread rapidly eastward along the Silk Road, overwhelmed Zoroastrianism, Judaism and Buddhism, and marched straight into Asia, and soon spread all over the Persian Gulf and as far away as the area ruled by Guishuang-that is, it has reached today’s Afghanistan.
Islamism
After conquering the Silk Road, Muslims gathered a lot of wealth and set off the most unforgettable academic research upsurge in history.
Many scholars were summoned to the Palace in Baghdad or attracted to the top academic centers all over Central Asia, engaged in mathematics, philosophy, physics, geography and other research. At that time, the radicals were not Muslims, but Christians; At that time, those wise men who were open-minded, curious and generous were all on the Silk Road, not Europe and America.
Silk Road and Global Economy

economic globalization
Along the Silk Road more than 2,000 years ago, in Carthage and other cities around the Mediterranean, the rich and powerful can wear silk handmade in China; Pottery produced in southern France can be found in England and the Persian Gulf. In kitchens in Xinjiang and Rome, condiments from India can be used; Greek characters can be carved on buildings in northern Afghanistan; In the east, you can see galloping horses in Central Asia.
We usually regard globalization as a unique phenomenon in contemporary society, but as early as two thousand years ago, globalization was already a fact, which provided opportunities, brought problems and promoted technological progress.
Great discovery of America
After the 16th century, with Columbus discovery of america, Europe got a lot of silver from America. The Silver Road encircles the world like a ribbon, but in the end it all flows to the same place through the Silk Road: China.
At the same time, Chinese porcelain and silk are very popular in Europe. With the influx of silver, the culture of the Ming Empire was unprecedentedly prosperous, with novels, operas, paintings and philosophy shining brilliantly. However, due to its inability to control inflation, the Ming Empire eventually collapsed.
The British Empire dominates.
In the 16th century, the success of Spain and Portugal frustrated the British. In order to gain a place on the Silk Road, Britain established some new trading companies, such as the Turkish company and the East India company. These companies all obtained royal charters, plundered the wealth on the Silk Road by their monopoly position, and finally created the glory of the empire that never sets.
Silk Road and Human War

Roman Persian war
For the Romans, if the empire wants to grow, it must have a large number of cities, thus collecting enough taxes; If the empire wants to be brilliant, it must have artists and craftsmen. These did not exist in the barren European continent at that time. In order to build a powerful empire, the Romans must control the heart of the world-the Silk Road. In order to achieve this goal, Rome and Persia fought for 400 years.
The crusades
Although the 200-year-long Crusade is regarded as a religious war, there is a more important secular power behind it-the infinite wealth on the Silk Road. Relying on the opportunity of the crusade, cities such as Venice rose to become upstarts on the Silk Road, and the west also re-entered the core area of the world.
The Mongols are coming.
The Mongolian iron hoof conquered almost the whole Eurasia along the Silk Road. As well known as the horrible massacre, it is the wisdom of Mongols to rule the world.
They encouraged trade across Europe and Asia on the Silk Road with low tax rates, eliminated ethnic barriers on the Silk Road with military rule, promoted the integration of eastern and western civilizations, and created freedom and prosperity of religious belief on the Silk Road with tolerant policies.
Nazi road
On August 23, 1939, the Soviet Union and Nazi Germany signed the Soviet-German Non-aggression Treaty, although the alliance between the two countries was incredible. But in fact, Stalin compromised with Germany in order to gain time, and he needed time to restore the turbulent country.
The other ally, Hitler, was for wheat and oil located in the south of the Soviet Union, two crops located at the western end of the Silk Road, which were extremely scarce in Germany.
Hitler’s original wishful thinking was to form an alliance with the Soviet Union, which provided supplies. Unexpectedly, after the war began, Stalin did not fully support Germany, but fell to the allies. In the end, Hitler was forced on an adventurous road to invade the Soviet Union, which doomed the collapse of the Third Reich.
Today, despite frequent wars and constant frictions, the Silk Road passes through Islam and other places, but in Peter Franco Pan’s view, its important role in natural resources, geographical location, history and culture still exists, and the Silk Road is reviving.