Is the high temperature abnormal in the north? How long will it last? Chief Detailed Response of National Climate Center
During the Dragon Boat Festival holiday, large-scale and persistent high temperature weather occurred in northern China. From 8: 00 to 16: 00 on June 22, high temperature weather above 35℃ occurred in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, Shandong, central and northern Henan, northern Anhui, northern Jiangsu, western Inner Mongolia, eastern Xinjiang and southern Xinjiang basin.
Among them, the temperature in Beijing, Tianjin, central Hebei, northern Shandong and other places rose rapidly, with the highest temperature rising above 40℃, and the local temperature in Huairou, Beijing and Binhai, Tianjin reached 41.8℃. The highest temperatures in 17 national meteorological observatories in Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei and Shandong exceeded historical extremes.
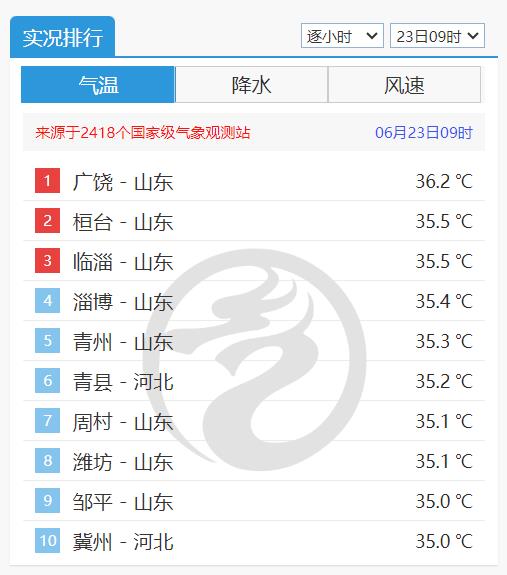
The national temperature list at 9: 00 on June 23rd, below 35℃, is difficult to be listed.
"It’s too hot!" Many tourists who travel during the holidays call directly on the Internet.
After comprehensive judgment and emergency consultation, China Meteorological Bureau launched a four-level emergency response to major meteorological disasters (high temperature) at 09: 00 on the 23rd. The Central Meteorological Observatory continued to issue a high-temperature orange warning this morning, and the Beijing Meteorological Observatory also upgraded to issue a high-temperature red warning signal this morning.
Is this round of high temperature abnormal in the north? What is the cause of such hot weather? How long will it last? Will it get hotter in July and August? On the afternoon of June 23rd, experts from the National Meteorological Center responded to these hot spots when interviewed by The Paper.
For the first time since the establishment of Beijing Observatory, it has exceeded 40℃ for two consecutive days.
Influenced by the warm air mass and strong solar radiation, high temperature above 39℃ occurred in most parts of Beijing on the 22nd, and the highest temperature in the observatory was 41.1℃, which exceeded the historical extreme in June (the extreme maximum temperature in the observatory in June was 40.6℃, which appeared on June 10th, 1961). Among the 556 meteorological monitoring stations in the city, 454 stations have the highest temperature of 39℃ and above, and 265 stations have the highest temperature of 41℃ and above.
By 14: 00 p.m. on 23rd, the temperature in the observatory had reached 40℃ (at 13: 36), and the highest temperature in 305 of the 556 meteorological monitoring stations in the city was 39℃ and above, and the highest temperature in 158 stations was 40℃ and above.
"For the first time since the observatory was built, it has exceeded 40 C for two consecutive days." Zhang Yingxin, chief forecaster of Beijing Meteorological Observatory, said that under the control of strong heating air mass, the high temperature weather continued from 23rd to 25th, and the highest temperature in most areas was 37℃ to 40℃. Among them, the highest temperature can reach about 40℃ from 23rd to 24th. The Beijing Meteorological Observatory upgraded and released the high temperature red warning signal at 07: 00 on June 23rd.
Zhang Yingxin said that this round of high temperature in Beijing has strong intensity and long duration. The main reasons are as follows: First, the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region began to be controlled by the heating mass on the 21st, and the heating mass was strong and affected for a long time; Second, under the control of the high-pressure ridge situation, the sky is clear and partly cloudy, and there is no cloud cover, so the radiation warming is more favorable and promotes the warming; Third, it has just entered the summer solstice solar term, with the longest daylight, and long-term sunshine is conducive to the emergence and maintenance of high temperature; Fourth, the air humidity is small and the weather is dry, which is also conducive to the temperature rise.
Since June, 46 national meteorological stations in China have broken historical extremes.
Since June this year (as of the 22nd), the daily maximum temperature of 183 national meteorological stations in China has exceeded the monthly extreme value, 46 stations have exceeded the historical extreme value, and the daily maximum temperature in North China has exceeded the historical extreme value on June 22nd.
Since June this year (as of the 22nd), the number of high temperature days in North China has been 6.4 days, 3.1 days more than the normal period (3.3 days), ranking fifth in history since 1961, after 1972, 1968, 2005 and 2022. Beijing (7.9 days) is the largest in the same period since 1961, followed by Hebei (7.8 days) and Tianjin (6.1 days).
It’s only at the end of June. Will the temperature be higher in July and August?
In this regard, Gao Hui, chief forecaster of the National Climate Center, told The Paper that since June (as of the 22nd), the 35℃ high temperature weather in China is mainly distributed in North China, central and western South China and most of Xinjiang. Among them, the number of high temperature days in North China is mostly 6-10 days, and the number of high temperature days in western Hebei reaches more than 10 days. Compared with the same period of normal years, the number of high temperature days in these areas is 3-5 days more, and that in Beijing, southwest Hebei and other places is more than 5 days.
Gao Hui said that there are obvious regional differences in high temperature concentration periods in different parts of China. For North China, high temperature weather is usually more likely to occur from June to early July before the rainy season, and high temperature for several days in a row is also common in June. This period of time is mainly dry-hot high temperature, which is characterized by high temperature and low humidity.
In the late July, with the subtropical high jumping northward and the summer monsoon advancing northward, the water vapor transport and atmospheric humidity increase, and the cloud cover will also increase, and there will be sultry weather, that is, humid and hot high temperature. As far as the highest temperature is concerned, the highest temperature in the previous period is usually higher than that in the latter period. However, it should also be noted that the somatosensory temperature of human body is not only related to temperature, but also affected by humidity. Often, this humid and hot high temperature will aggravate the somatosensory temperature of human body.
Under the background of global warming, the probability of high temperature breaking the historical extreme value is greater.
Gao Hui said that under the background of global warming, the frequency of extreme high temperature is increasing rapidly in both the south and the north. According to the forecast of the National Climate Center, the temperature in North China and Huanghuai is high this summer, which is accompanied by an increase in the number of high-temperature days, so there is a great probability that the north will be hotter than normal this summer. In this case, it is also possible for some stations to break the historical extreme value.
This year is the development year of El Ni? o events. Is the high temperature in the north related to El Ni? o events? Gao Hui responded to The Paper that it has entered the state of El Nino, but the influencing factors of high temperature in the north in early summer are complex and cannot be simply attributed to El Nino. "For example, in the middle and late June last year, the high temperature in the northern region was more extreme, but last year was the year of La Nina. Moreover, the existing scientific research results also show that the high temperature in the north in early summer is more susceptible to the SST in the North Atlantic and the atmospheric circulation in the middle and high latitudes. "
Zhang Fanghua, chief forecaster of the National Meteorological Center, said in an interview with The Paper that recently, there have been two high-temperature weather processes in North China, Huanghuai and other places. The high temperature intensity is high and lasts for a long time. There are four main reasons. First, North China, Huanghuai and other places are controlled by a strong heating mass, and its influence time is longer; Secondly, under the control of the high-pressure ridge, the sky is clear and partly cloudy, and the warming of solar radiation is more favorable and promotes the warming; Third, it is the summer solstice solar term, and the daytime is relatively long, that is, the sun shines for a long time during the day, which is conducive to the rise of temperature and the emergence and maintenance of high temperature; Fourth, in North China, Huanghuai and other places, the air humidity is small and the weather is dry, which is also conducive to the temperature rise.
Zhang Fanghua said that after this round of high temperature, it is expected that there will be high temperature weather in North China, Huanghuai and other places from the 27th to the 30th.
Beware of heatstroke in hot weather.
What impact will it bring to public health when the Dragon Boat Festival holiday is hot again?
Liu Yanxiang, chief public service officer of the Public Meteorological Service Center of China Meteorological Administration, said that the most direct adverse impact of high temperature weather on health is high temperature heatstroke. When there are symptoms of threatened heatstroke and mild heatstroke, there will be symptoms such as headache, dizziness, thirst, hyperhidrosis, weakness and soreness of limbs, inattention and uncoordinated movements. If you move to a cool place in time and replenish water, the symptoms will be alleviated. However, if severe heatstroke occurs, it may cause arrhythmia, coma, convulsion, rhabdomyolysis, acute renal failure, liver failure, hypotension, shock, arrhythmia and heart failure, pulmonary edema and brain edema. Severe heatstroke, especially heatstroke, has a high risk of death.
There are also two types of heatstroke, one is labor-induced heatstroke, which is mainly caused by the imbalance between heat production and heat dissipation caused by high-intensity physical activity. Healthy young people who are common in strenuous outdoor exercise in summer, such as officers and soldiers, athletes, firefighters, construction workers, couriers, etc. The other is the classic heatstroke, which is mainly caused by the imbalance between heat production and heat dissipation caused by passive exposure to the thermal environment. It is common in young people, pregnant women and the elderly, and people with chronic basic diseases or low immune function. In addition, hot and stuffy rooms and cars without air conditioning are also places where heatstroke often occurs.
Liu Yanxiang suggested that the human body sweats a lot in high temperature weather, which causes the blood viscosity to increase and the blood flow speed to slow down, which leads to an increase in heart load and an increase in the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.